Gallbladder 14
GB14 Acupressure Point
Acupressure point Gallbladder 14 has limited uses compared to other points on the GB channel, but it is an important point for pain of the forehead. 
Related Articles
- The Wood Element of Traditional Chinese Medicine Explained
- General Acupressure Directions-Video
- Natural Therapies for Bell's Palsy
- Natural Therapies for Eye Conditions
- Natural Therapies for Headaches
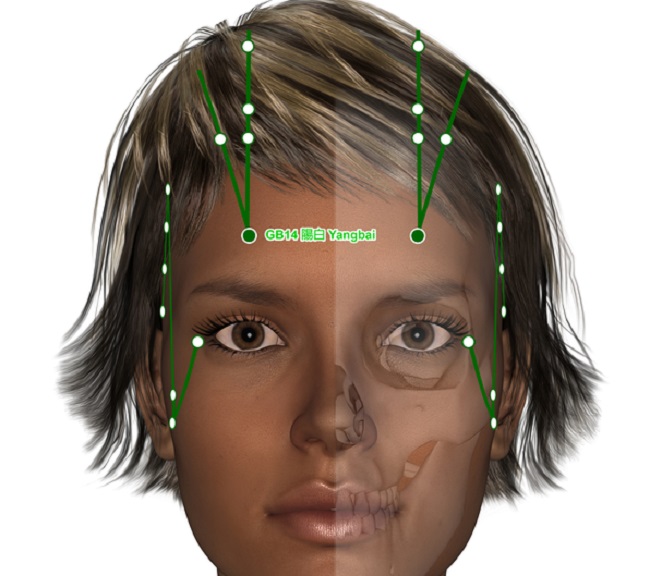
Location of Acupressure Point GB 14
On the forehead directly above the eyebrows one Cun superior to midpoint of eyebrow lining up with the pupil when one is looking straight ahead. Apply the Head-Ease Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Gallbladder 14 to activate the healing potential of the pressure point.
Traditional Chinese Medicine Indications and Acupressure Point Combinations Using Gallbladder 14
Headache
In the case of frontal headaches:
- Apply the Head-ease Acupressure Stick to acupressure point Gallbladder 14
- Apply the Wood Element Acupressure Stick to acupressure point Gallbladder 41
Twitching Eyes
With chronic twitching eyes due to Liver-Wind rising:
- Apply the Wood Element Acupressure Stick to acupressure point Gallbladder 14
- Apply the Wood Element Acupressure Stick to acupressure point Gallbladder 41
- Apply the Wood Element Acupressure Stick to acupressure point Liver 2
Drooping Eyelids
With drooping eye lids with aging:
- Apply the Wood Element Acupressure Stick to acupressure point Gallbladder 14
- Apply the Earth Element Acupressure Stick to acupressure point Spleen 3
- Apply the Earth Element Acupressure Stick to acupressure point Stomach 44
- Apply the Water Element Acupressure Stick to acupressure point Bladder 62
Bell's Palsy
For drooping eyelids due to Bell's Palsy and External/Internal Wind:
- Apply the Wood Element Acupressure Stick to acupressure point Gallbladder 14
- Apply the Wood Element Acupressure Stick to acupressure point Liver 2
- Apply the Wood Element Acupressure Stick to acupressure point Gallbladder 41
![]()
Other Name(s) of GB 14
- Yangbai
- Yang White
Traditional Chinese Medicine Classifications of GB 14
- Meeting Point of Gallbladder, Stomach, Yang Wei, Triple Burner and Large Intestine Channel
Traditional Chinese Medicine Actions or GB 14
Cautions: Do not use acupressure as self-care when pregnant without the guidance of a licensed acupuncturist. Always discuss new treatment modalities with your local health care professional.
![]()
Li, X., Chen, C., Zhao, C., Li, Z., Liang, W., & Liu, Z. (2018). Augmentation effect of acupuncture on Bi'nao for hypophasis in patients with Bell's palsy: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials, 19(1), 316. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-018-2699-z
Farahmand, S., Shafazand, S., Alinia, E., Bagheri-Hariri, S., & Baratloo, A. (2018). Pain Management Using Acupuncture Method in Migraine Headache Patients; A Single Blinded Randomized Clinical Trial. Anesthesiology and pain medicine, 8(6), e81688. https://doi.org/10.5812/aapm.81688
Li, K., Zhang, Y., Ning, Y., Zhang, H., Liu, H., Fu, C., Ren, Y., & Zou, Y. (2015). The effects of acupuncture treatment on the right frontoparietal network in migraine without aura patients. The journal of headache and pain, 16, 518. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10194-015-0518-4
Li, P., Qiu, T., & Qin, C. (2015). Efficacy of Acupuncture for Bell's Palsy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. PloS one, 10(5), e0121880. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0121880
He, X., Zhu, Y., Li, C., Park, K., Mohamed, A. Z., Wu, H., Xu, C., Zhang, W., Wang, L., Yang, J., & Qiu, B. (2014). Acupuncture-induced changes in functional connectivity of the primary somatosensory cortex varied with pathological stages of Bell's palsy. Neuroreport, 25(14), 1162–1168. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNR.0000000000000246
