Large Intestine 20
LI20 Acupressure Point Location and Uses
Use the Sinus Aroma Acu-Stick® to activate acupuncture point Large Intestine 20. LI 20 acupressure point on the Hand Taiyiang, or Large Intestine channel has limited uses mainly associated with the nose and sinusitis.
Related Articles:
- Learn How Aroma Acu-Therapy Works
- The Metal Element of Chinese Medicine
- How traditional Chinese medicine addresses Sinusitis
- General Acupressure Directions-Video
![]()
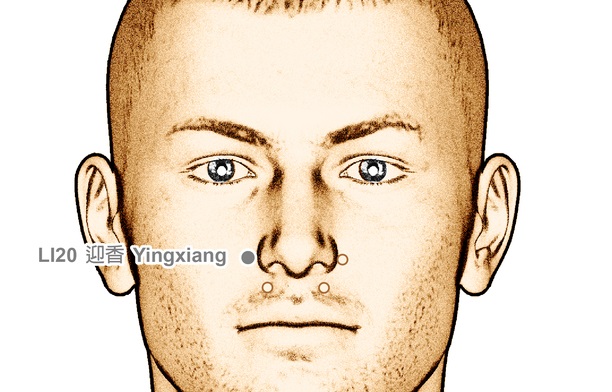
Location of Acupressure Point LI 20
On the face at the lateral border ali nasi of the nose in the naso-labial groove, at the level of the midpoint. Apply the Sinus Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Large Intestine 20 to activate the healing potential of the pressure point.
![]()
Traditional Chinese Medicine Indications and Acupressure Point Combinations for Acupressure Point LI 20
Breathing
- Nasal congestion with no discharge combine acupressure point Large Intestine 20, acupressure point Large Intestine 4 and acupressure point Bitong using the reducing or dispersing method (counterclockwise motion) with the Sinus Acupressure Stick at LI 20 and the Metal Element Acupressure Stick at LI 4, the Metal Acupressure Stick at acupressure point Large Intestine 4
- Nasal congestion and copious clear discharge combine acupressure point Large Intestine 20, acupressure point Large Intestine 4 and acupressure point Stomach 40 using the reducing or dispersing method (counterclockwise motion) with the Sinus Acupressure Stick at LI 20 and the Metal Element Acupressure Stick at LI 4, the Earth Acupressure Stick at Stomach 40
- Nasal congestion and dark green or orange discharge as with sinus infections combine acupressure point Large Intestine 20, acupressure point Large Intestine 4 and acupressure point Large Intestine 11 using the reducing or dispersing method (counterclockwise motion) with the Sinus Acupressure Stick at LI 20 and the Metal Element Acupressure Stick at LI 4, the Metal Acupressure Stick at Large Intestine 4
Allergies
Chronic seasonal allergies with sinusitis and sneezing combine acupressure point Large Intestine 20, acupressure point Large Intestine 4 and acupressure point Lung 10 using the reducing or dispersing method (counterclockwise motion) and Stomach 36 using the tonification method (clockwise motion) with the Sinus Acupressure Stick at LI 20 and the Metal Element Acupressure Stick at LI 4, the Earth Acupressure Stick at Stomach 44
Sense of Smell
- Loss of the sense of smell combine acupressure point Large Intestine 20, acupressure point Large Intestine 4, acupressure point Lung 7, and Stomach 36 using the tonification method (clockwise motion) with the Sinus Acupressure Stick at LI 20, the Earth Acupressure Stick at Stomach 36 and the Metal Element Acupressure Stick at Lung 7
Nasal Polyps
- Nasal polyps combine acupressure point Large Intestine 20, acupressure point Bitong, and acupressure point Stomach 36 using the tonification method (clockwise motion) with the Sinus Acupressure Stick at LI 20 and Bitong, the Earth Acupressure Stick at Stomach 44
Sinus Soreness
Nasal passage sores due to chronic Stomach Fire with hunger and no desire to eat combine acupressure point Large Intestine 20, acupressure point Stomach 44 and acupressure point Large Intestine 11 using the reducing or dispersing method (counterclockwise motion) with the Sinus Acupressure Stick at LI 20, the Earth Acupressure Stick at Stomach 44 and the Metal Element Acupressure Stick at Large Intestine 11
Sneezing
Sneezing uncontrollably combine acupressure point Large Intestine 20, acupressure point Large Intestine 4 and acupressure point Lung 10 using the reducing or dispersing method (counterclockwise motion) and Stomach 36 using the tonification method (clockwise motion) and apply our Metal Element Acupressure Stick to LI 4 and LU 10 and apply the Sinus Acupressure Stick to LI 20
Nosebleed
Nosebleed due to chronic Stomach Fire with hunger and no desire to eat combine acupressure point Large Intestine 20, acupressure point Stomach 44 and acupressure point Liver 2 using the reducing or dispersing method (counterclockwise motion) applying the Wood Element acupressure Stick to LV 2 and apply the Earth Element Acupressure Stick to ST 44
Facial Paralysis or Swelling
- Deviation of the mouth as with Bell’s Palsy due to External Wind combine acupressure point Large Intestine 20, acupressure point Stomach 44 and acupressure point Large Intestine 4 using the reducing or dispersing method (counterclockwise motion) and acupressure point Stomach 36 using the tonification method (clockwise motion) and apply our Bell’s Palsy Plaster topically to face
- Swelling and itching of the face that comes on suddenly due to Internal or External Wind combine acupressure point Large Intestine 20, acupressure point Stomach 44 and acupressure point Large Intestine 4 using the reducing or dispersing method (counterclockwise motion) add the Internal Wind Foot Soak for Internal Wind
Lips
- Dry lips with cracking due to chronic Stomach Fire with hunger and no desire to eat combine acupressure point Large Intestine 20, acupressure point Stomach 44 and acupressure point Large Intestine 11 using the reducing or dispersing method (counterclockwise motion)
- Pain and swelling of the lip with cold sores combine acupressure point Large Intestine 20, acupressure point Stomach 44 and acupressure point Large Intestine 11 using the reducing or dispersing method (counterclockwise motion) and acupressure point Stomach 36 using the tonification method (clockwise motion) and use the Cold-sore Stick topically
![]()
Traditional Chinese Medicine Actions of Acupressure Point LI 20
- Benefits the nose, relieves congestion
- Opens nasal passages and sinuses
- Benefits respiration
- Improves functional capacity of the Lung
- Benefits the face
Other Name(s) of Acupuncture Point LI 20
- Welcome Fragrance
- Surging Yang
- Encounters Perfume
- Thoroughfare Yang
Traditional Chinese Medicine Classifications of Acupressure Point Large Intestine 20
- Exit Point of the Large Intestine Channel Connecting to Acupuncture Point Stomach 1
- Crossing Point with the Stomach Channel
- Meeting of Large Intestine with Stomach, Stomach Divergent and Spleen Divergent Channels
Cautions: Do not use acupressure as self-care when pregnant without the guidance of a licensed acupuncturist. Always discuss new treatment modalities with your local health care professional.
![]()
Liebell D. (2019). Waking Up and Literally Smelling the Coffee: Inducing Olfactory Function with 3-Phase Auricular Therapy. Medical acupuncture, 31(1), 45–48. doi:10.1089/acu.2018.1326
Stavem, K., Røssberg, E., & Larsson, P. G. (2008). Health-related quality of life in a trial of acupuncture, sham acupuncture and conventional treatment for chronic sinusitis. BMC research notes, 1, 37. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-1-37
Elaissi, A., Rouis, Z., Salem, N. A., Mabrouk, S., ben Salem, Y., Salah, K. B., … Khouja, M. L. (2012). Chemical composition of 8 eucalyptus species' essential oils and the evaluation of their antibacterial, antifungal and antiviral activities. BMC complementary and alternative medicine, 12, 81. doi:10.1186/1472-6882-12-81
Dai, Q., Pang, Z., & Yu, H. (2016). Recovery of Olfactory Function in Postviral Olfactory Dysfunction Patients after Acupuncture Treatment. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM, 2016, 4986034. doi:10.1155/2016/4986034
Tanaka O1, Mukaino Y. The effect of auricular acupuncture on olfactory acuity. Am J Chin Med. 1999;27(1):19-24.
This information has not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This information is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
