Incontinence
Urinary Incontinence and Chinese Medicine
 Urinary incontinence is a common condition with aging, especially among women who have had children. Common actions such as coughing, sneezing, or laughing can lead to embarrassing involuntary losses of urine with incontinence. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has been shown by scientific research effective in quelling incontinence. A major pattern of imbalance leading to incontinence as we age is waning Kidney Yang.
Urinary incontinence is a common condition with aging, especially among women who have had children. Common actions such as coughing, sneezing, or laughing can lead to embarrassing involuntary losses of urine with incontinence. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has been shown by scientific research effective in quelling incontinence. A major pattern of imbalance leading to incontinence as we age is waning Kidney Yang.
For best outcomes using self-care, combine associated Aroma Acu-Sticks® to acu-points, topical remedies, and good lifestyle practices.
![]()
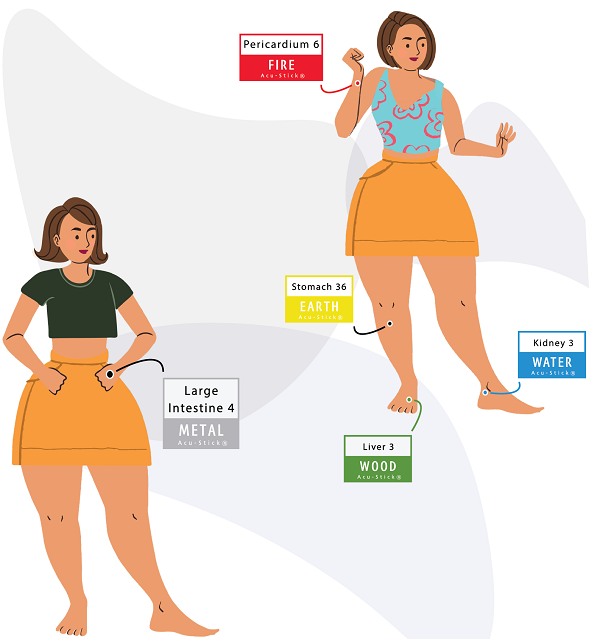
Aroma Acu-therapy™ for Incontinence
Kidney 3
Apply the Water Element Aroma Acu-Stick® to activate Acupressure Point KI 3
Why? Acu-point Kidney 3 is the Source Point of the Kidney energetic organ system that is closely associated with the Urinary Bladder according to Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Apply the Earth Element Aroma Acu-Stick® to activate Acupressure Point ST 36
Why? Acu-point Stomach 36 is the main Qi energy bolstering point of all of the organs of the body.
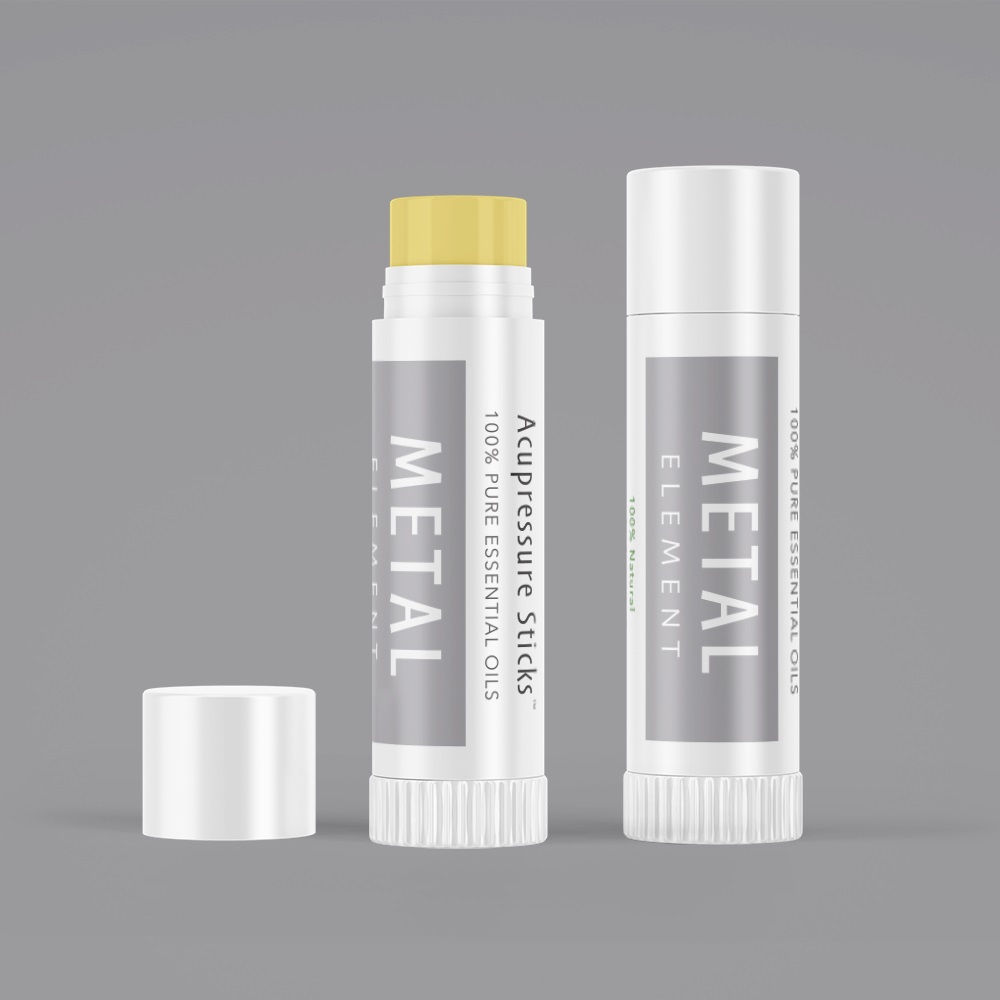
Apply the Metal Element Aroma Acu-Stick® to activate Acupuncture Point LI 4
Why? LI 4 works together with Liver 3 in its ability to insure the correct movement of Qi of the body as the famous point combination called the "Four Gates".
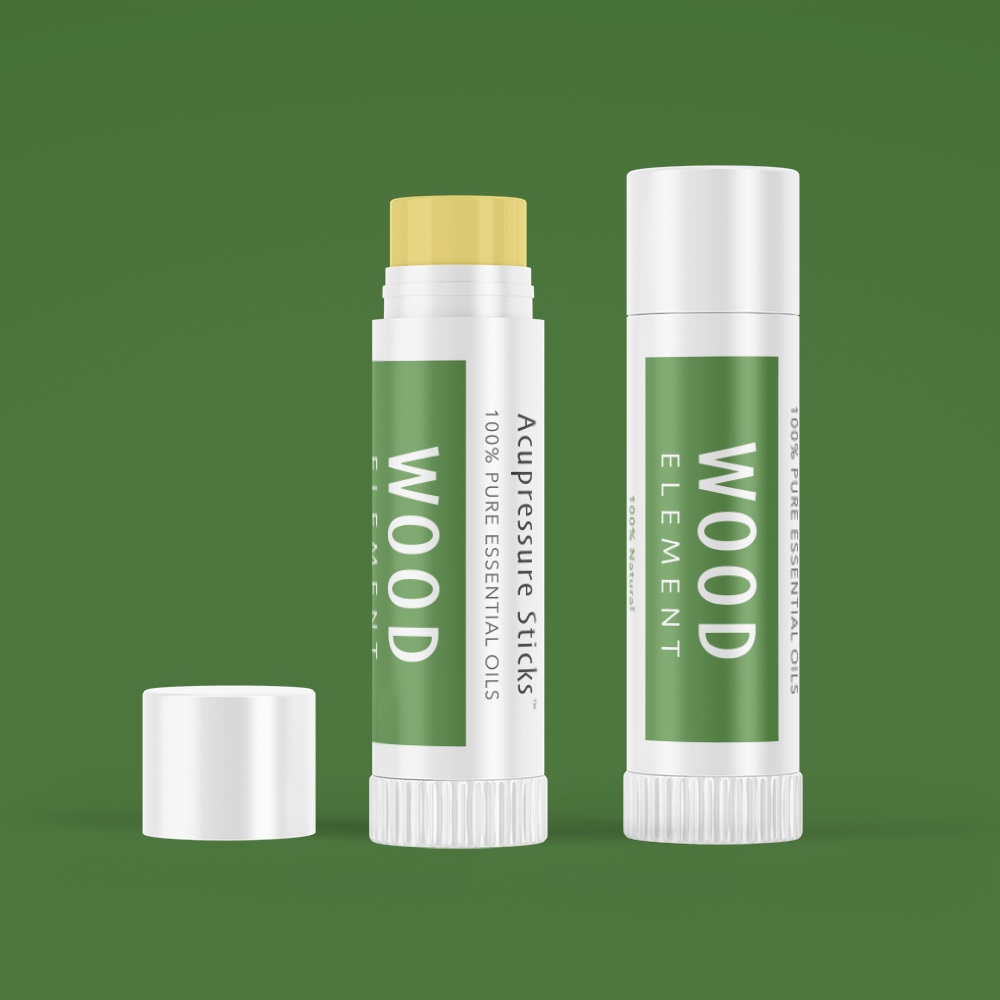
Apply the Wood Element Aroma Acu-Stick® to activate Acupressure Point LV 3
Why? The Wood Element is in charge of cultivating motivation in Chinese medicine and the Liver circulates Qi energy and acu-point Liver 3 is the energy source point for the Liver energetic organ system.
Apply the Fire Element Aroma Acu-Stick® to activate Acupuncture Point Pericardium 6
Why? Acu-point PER 6 is used for painful urination.
Related Articles:
Incontinence Constitutional Imbalances in Chinese Medicine According to Symptoms
It is not uncommon for incontinence to present with more than one of these patterns of imbalance since it is a chronic condition that likely affects multiple energetic organ systems.
![]()
Kidney Yin Deficiency and Urinary Incontinence
Bladder function and the Chinese medical Yin-Yang theory can also point to certain patterns of imbalance. The bladder’s ability to hold urine is a Yin function. With Kidney Yin Deficiency, the bladder will not be able to hold the urine with symptoms such as:
- Frequent or sudden urination or urgency incontinence
- Stress incontinence with a leakage of urine while lifting heavy objects, laughing, coughing, or sneezing
- Night sweats, low grade feverish feeling, dizziness, poor memory, nighttime urination, and dry mouth.
![]()
Kidney Yang Deficiency and Urinary Incontinence
Yang Deficiency would be common with urinary problems associated with prostate issues, but is also seen in women. Urinary incontinence associated with Kidney Yang Deficiency would include symptoms such as:
- Clear urine
- Profuse pale urination
- Lower backache
- A feeling of coldness throughout the body
- Impotence and decreased libido
![]()
 Liver Imbalances and Urinary Incontinence
Liver Imbalances and Urinary Incontinence
In Traditional Chinese Medicine, the Liver energetic organ system "governs the muscles and sinews" ; this means that the general function and health of the muscles are affected by Liver imbalances. Since muscles are involved with the ability to hold urine, an imbalance of the Liver can contribute to urinary incontinence or overactive bladder. Other signs of the Livers' involvement are indicated when the condition is worsened stressful situations or are accompanied by frustration or anger.
![]()
Qi Deficiency and Urinary Incontinence
In Chinese medicine, the Kidney energetic organ system "governs water", and is in charge of the metabolism of urination. Kidney Qi helps to hold the urine in the Bladder; therefore, Kidney Qi Deficiency could be the root cause of an urinary incontinence or an overactive bladder. Spleen Qi Deficiency can often lead to Qi Deficiency of other energetic organ systems of the body, symptoms could include:
- A feeling of bearing down
- Abdominal distention after eating
- Loose stools
- Internal Dampness
Lung Qi Deficiency and Incontinence
While not as common as the other patterns, Lung imbalances can be at the root of the cause of incontinence; here a couple of the reasons why:
- The Lungs and the Kidneys are closely interrelated in Chinese medicine, and an imbalance in one of the energetic organ systems can easily have an impact on the other.
- The Lung energetic organ system is central in the formation of Qi energy for the whole body, thus Spleen Qi Deficiency or Kidney Qi Deficiency could be related to Lung Deficiency.
You may notice incontinence occurring during asthma attacks or during coughing attacks with this pattern.
![]()
Stress Incontinence
The most common type of incontinence among women is stress incontinence with symptoms of involuntarily leaking urine while exercising, coughing, sneezing, laughing or lifting with the sudden pressure to the bladder causes urine to leak. While weaknesses due to childbirth to muscles that hold the bladder in place is the most common cause, a weakening of the bladder itself can also occur. Other causes of stress incontinence include:
- Nerve damage can be a result of or from treatment of gynecologic or pelvic cancers with surgery, radiation or chemotherapy, or can be due to diseases such as diabetes, stroke, Parkinson's disease and/or multiple sclerosis,
- Following menopause, a decrease in estrogen can weaken the sphincter muscle in women
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia, prostate cancer or prostate surgery can lead to stress incontinence in men
![]()
Robinson D. Patholophysiology of female lower urinary tract dysfunction. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 1998;25:747–756.
Philip T, Shah PJ, Worth PH. Acupuncture in the treatment of bladder instability. Br J Urol. 1988;61:490–493.
Yang BS, Ye DW, Yao XD, et al. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi (The study of acupuncture therapy for postprostatectomy incontinence). 2010;48(17):1325-1327.
Chang PL. Urodynamic studies in acupuncture in women with frequency, urgency, and dysuria. J Urol. 1988;140:563–566.
Bergström K, Carlsson C, Lindholm C, Widengren R. Improvement of urge- and mixed-type incontinence after acupuncture treatment among elderly women - a pilot study. J Auton Nerv Syst. 2000;79:173–180.
Knardahl S, Elam M, Olausson B, Wallin BG. Sympathetic nerve activity after acupuncture in humans. Pain. 1998;75:19–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Paik, S. H., Han, S. R., Kwon, O. J., Ahn, Y. M., Lee, B. C., & Ahn, S. Y. (2013). Acupuncture for the treatment of urinary incontinence: A review of randomized controlled trials. Experimental and therapeutic medicine, 6(3), 773–780. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2013.1210
This information has not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This information is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.





