Large Intestine 10
 LI10 Acupressure Point
LI10 Acupressure Point
Use the Metal Element Aroma Acu-Stick® to activate points on the Large Intestine Channel. Large Intestine 10 acupressure point does not have as many uses as acupressure points like LI 4, but it is a very important point for pain along the Large Intestine channel in the lower arm.
Related Articles:
- Learn How Aroma Acu-Therapy Works
- The Metal Element of Chinese Medicine
- How traditional Chinese medicine addresses Pain
- General Acupressure Directions-Video
![]()
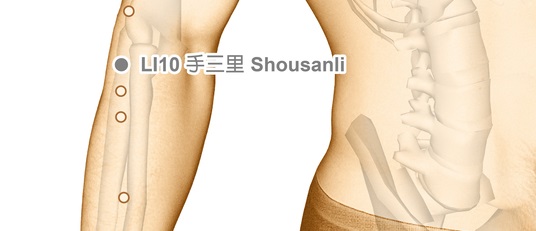
Location of Acupressure Point LI 10
Bring the hand to the chest with the thumb pointing up. Acupressure point Large Intestine 10 will be 2 Cun distal of the crease of the elbow on the line with the thumb on the radial surface of the forearm if the hand is placed on the chest. Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Large Intestine 10 to activate the healing potential of the pressure point.
Acupressure Point Combinations with LI 10 for Specific Health Conditions
Pain
Pain and immobility of the arm treatments often use “The Chain and Lock Method” of choosing three acupressure points that support each other along the same channel.
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Large Intestine 10
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Large Intestine 11
Pain and immobility of the shoulder:
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Large Intestine 10
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Large Intestine 11
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Large Intestine 4
- Apply the Earth Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Stomach 38
Pain of the thumb, pointer finger, and/or wrist due to a competitive stress injury:
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Large Intestine 10
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 10
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Large Intestine 4
Paralysis
Paralysis of the arm due to a stroke:
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Large Intestine 10
- Apply the Fire Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Pericardium 6
- Apply the Earth Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Stomach 36
- Apply the Earth Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Spleen 6
- Apply the Water Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Bladder 40
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Large Intestine 4
- Apply the Wood Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Gallbladder 20
Numbness
Numbness of the lower arm:
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Large Intestine 10
- Apply the Earth Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Stomach 36
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Large Intestine 4
- Apply the Wood Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Liver 3
Lymphatic Congestion
Lymph congestion due to lymph node removal in arm (pit):
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Large Intestine 10
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Large Intestine 4
- Apply the Wood Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Liver 3
Atrophy
Atrophy of the muscles of the lower arm:
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Large Intestine 10
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Large Intestine 4
- Apply the Earth Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Spleen 6
- Apply the Earth Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Stomach 36
Other indications for Acupressure Point LI 10
- An inability to extend the elbow or contract and flex the elbow
- Acute lower back pain
- Acute knee pain
- Abdominal pain, vomiting
- Stagnant Qi of the Stomach due to overuse of antacids to treat acid reflux
- Diarrhea, periodic sensation of cold in the intestines
- Toothache pain of the upper jaw
- Pain in lateral elbow, wrist and hand
- Combined with St-36 and Ren-11 to make the "Three Li for Deficiency” of the Spleen and Stomach
![]()
Other Name(s) of Acupuncture Point LI 10
- Arm Three Li
- Upper Three Li
- Ghost Evil
- Third Mile
- Arm Three Mile
Traditional Chinese Medicine Classifications of Acupuncture Point LI 10
None
Traditional Chinese Medicine Actions of Acupressure Point Large Intestine 10
- Regulates and invigorates Qi and moves Blood of the Large Intestine channel
- Activates the Large Intestine channel and alleviates pain
- Softens masses due to stagnation in the Large Intestines and Stomach energetic organ systems
Cautions: Do not use acupressure as self-care when pregnant without the guidance of a licensed acupuncturist. Always discuss new treatment modalities with your local health care professional.
![]()
Wang, G., Jia, S., Liu, M., Song, X., Li, H., Chang, X., & Zhang, W. (2020). Impact of local thermal stimulation on the correlation between oxygen saturation and speed-resolved blood perfusion. Scientific reports, 10(1), 183. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-57067-6
Yang, S., Li, T., Yang, H., Wang, J., Liu, M., Wang, S., … Jiang, B. (2020). Association between muscle strength and health-related quality of life in a Chinese rural elderly population: a cross-sectional study. BMJ open, 10(1), e026560. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2018-026560
Li, S., Xie, P., Liang, Z., Huang, W., Huang, Z., Ou, J., … Chai, S. (2019). Corrigendum to "Efficacy Comparison of Five Different Acupuncture Methods on Pain, Stiffness, and Function in Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Network Meta-Analysis". Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM, 2019, 3713197. doi:10.1155/2019/3713197
Zheng, H., Chen, R., Zhao, X., Li, G., Liang, Y., Zhang, H., & Chi, Z. (2019). Comparison between the Effects of Acupuncture Relative to Other Controls on Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis. Pain research & management, 2019, 2871505. doi:10.1155/2019/2871505
Lv, J. Q., Wang, C., Yang, Y., Li, Y., Xu, T. H., & Jian, L. Q. (2019). Intradermal thumbtack needle buried Neiguan (P6) point for prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting in patients undergoing craniotomy: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. BMJ open, 9(11), e032417. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2019-03241
This information has not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This information is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.

