Lung 9
Acupressure Point LU9 Location and Uses
Use the Metal Element Aroma Acu-Stick® to activate points on the Lung Channel. Lung 9, also referred to as LU 9 acupressure point is the source point on the Hand Tai Yin, or Lung channel, which means it is a major point for tonifying Lung Qi and Lung Yin. It can be used in a variety of conditions including breathing and lung problems, and pain along the Lung meridian.
Related Articles:
- Learn How Aroma Acu-Therapy Works
- The Metal Element of Chinese Medicine
- How traditional Chinese medicine addresses Lung health
- General Acupressure Directions-Video
![]()
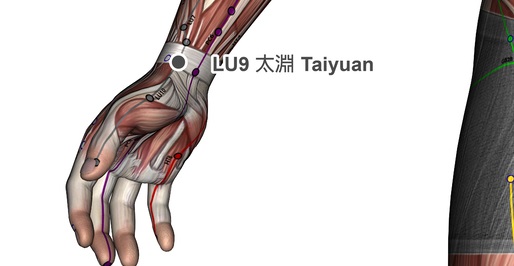
Location of Acupressure Point LU 9
At the wrist joint on the crease in inside the wrist (palm up) in the dip between the radial artery and the tendon. Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 9 to activate the healing potential of the pressure point.
Health Conditions Treated with Acupressure Point LU 9
Coughing
Cough with dark phlegm:
- Apply the Metal Element Aroma Acu-Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 9
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 10
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Large Intestine 11
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 9
- Apply the Earth Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Stomach 40
- Apply the Earth Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Spleen 9
Coughing of blood:
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 9
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 10
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Large Intestine 11
Asthma with inability to inhale or take a deep breath:
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 9
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 7
- Apply the Water Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Kidney 6
- Apply the Water Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Kidney 3
Wheezing, especially when tired:
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 9
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 7
- Apply the Water Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Kidney 6
- Apply the Water Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Kidney 3
Shortness of breath with adrenal fatigue:
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 9
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 7
- Apply the Water Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Kidney 6
- Apply the Water Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Kidney 3
Breathing difficulties following long illness and convalescence:
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 9
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 7
- Apply the Water Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Kidney 6
- Apply the Water Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Kidney 3
Lung conditions of a chronic nature such as bronchitis or COPD:
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 9
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 7
- Apply the Water Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Kidney 6
- Apply the Water Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Kidney 3
Agitation with breathing struggles:
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 9
- Apply the Wood Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Liver 3
- Apply the Fire Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Heart 8
Pneumonia
Oppression of the chest with difficult breathing and inability to lie down as with pneumonia:
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 9
- Apply the Earth Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Stomach 40
- Apply the Earth Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Spleen 9
Chronic Yawning
Yawning excessively around 3 PM:
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 9
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 7
- Apply the Water Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Kidney 3
Kidney Yin Deficient Cough
Dry throat with dry cough:
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 9
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 7
- Apply the Water Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Kidney 6
- Apply the Water Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Kidney 3
Wrist Weakness
Weakness or pain of the wrist:
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 9
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 7
- Apply the Fire Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Small Intestine 5
- Apply the Fire Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Pericardium 6
Shoulder Pain
Pain of the shoulder and upper back (scapula):
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 9
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Large Intestine 10
- Apply the Fire Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Small Intestine 3
Arm Pain
Pain in the medial aspect of the arm:
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 9
- Apply the Fire Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Pericardium 6
Bi-polar Disorder
Mania stage of manic depression:
combine acupressure point Lung 9 with acupressure point Heart 8 and acupressure point Pericardium 8
Rebellious Stomach Qi with vomiting combine acupressure point Lung 9 with acupressure point Pericardium 6
Chronic Burping
For unrelenting belching:
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 9
- Apply the Earth Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Ren 12
Eye Problems
Superficial visual obstruction, redness and pain of the eyes:
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 9
- Apply the Wood Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Liver 2
- Apply the Wood Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Liver 3
External Wind Cold Pathogenic Invasion
Cold feeling in the body and limbs with shivering not from an external pathogen such as the cold or flu:
combine acupressure point Lung 9 with acupressure point Stomach 36 and Spleen 3 applying the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to LU 9 and Earth Element Acupressure Stick to SP 3, ST 36
Tooth Pain
Toothache, head wind, swelling of the face:
combine acupressure point Lung 9 with acupressure Large Intestine point 11 and acupressure point Lung 10
Breast Pain
Breast pain from labored breathing and oppression:
with acupressure point Spleen 9 and acupressure point Lung 10
Nausea
In cases of altitude sickness or motion sickness:
- combine acupressure point Lung 9 with acupuncture point Pericardium 6
Nausea and vomiting with food poisoning:
- combine acupressure point Lung 9 with acupressure point Pericardium 6 and acupressure point Lung 7 applying the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to LU 9 and the Fire Element Acupressure Stick to PC 6
Trauma
First Aid for concussion or shock:
combine acupressure point Lung 9 with acupuncture point Heart 9 and with acupressure point Pericardium 6 and seek medical attention applying the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to LU 9 and the Fire Element Acupressure Stick to PC 6
![]()
Traditional Chinese Medicine Actions of Acupressure Point Lung 9
- Tonifies the Lung Qi and transforms phlegm
- Promotes the descending function of the lung
- Activates the channel and alleviates pain
- Regulates and harmonizes the one hundred vessels
Other Name(s) of Acupuncture Point Lung 9
- Taiyuan
- Great Abyss
- Supreme Abyss
- Very Great Abyss
- Ghost Heart
- Great Spring
Traditional Chinese Medicine Classifications of Acupoint Lung 9
- Stream Point
- Earth Point
- Source Point
- Gathering Point of the Blood Vessels
- Point of Cheng
- Influential Point of the Pulse
Cautions: Do not use acupressure as self-care when pregnant without the guidance of a licensed acupuncturist. Always discuss new treatment modalities with your local health care professional.
 References
References
Lu, K., Cheng, M. C., Ge, X., Berger, A., Xu, D., Kato, G. J., & Minniti, C. P. (2014). A retrospective review of acupuncture use for the treatment of pain in sickle cell disease patients: descriptive analysis from a single institution. The Clinical journal of pain, 30(9), 825–830. doi:10.1097/AJP.0000000000000036
Landgren, K., Tiberg, I., & Hallström, I. (2015). Standardized minimal acupuncture, individualized acupuncture, and no acupuncture for infantile colic: study protocol for a multicenter randomized controlled trial - ACU-COL. BMC complementary and alternative medicine, 15, 325. doi:10.1186/s12906-015-0850-x
Liu, Z., Liu, Y., Xu, H., He, L., Chen, Y., Fu, L., … Liu, B. (2017). Effect of Electroacupuncture on Urinary Leakage Among Women With Stress Urinary Incontinence: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA, 317(24), 2493–2501. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.7220
Wu, X. K., Stener-Victorin, E., Kuang, H. Y., Ma, H. L., Gao, J. S., Xie, L. Z., … PCOSAct Study Group (2017). Effect of Acupuncture and Clomiphene in Chinese Women With Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA, 317(24), 2502–2514. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.7217
Ngai SP1, Jones AY, Cheng EK. Lung meridian acupuncture point skin impedance in asthma and description of a mathematical relationship with FEV1. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2011 Dec 15;179(2-3):187-91. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2011.08.004.
This information has not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This information is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.

