Organ Systems
Zang–Fu Organs in Traditional Chinese Medicine
The concept of the organs in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) is radically different from that of contemporary western medicine. Understanding this difference is very important because the physiology and pathology of the Organs is fundamental to the understanding and treatment of disease.
Chinese medical theory is not a quick study, but we have tried to break it down for you throughout this website so that you can be a better advocate for your own health and well-being. For best outcomes using self-care, combine associated Aroma Acu-Sticks® to acu-points, topical remedies, and good lifestyle practices.
![]()
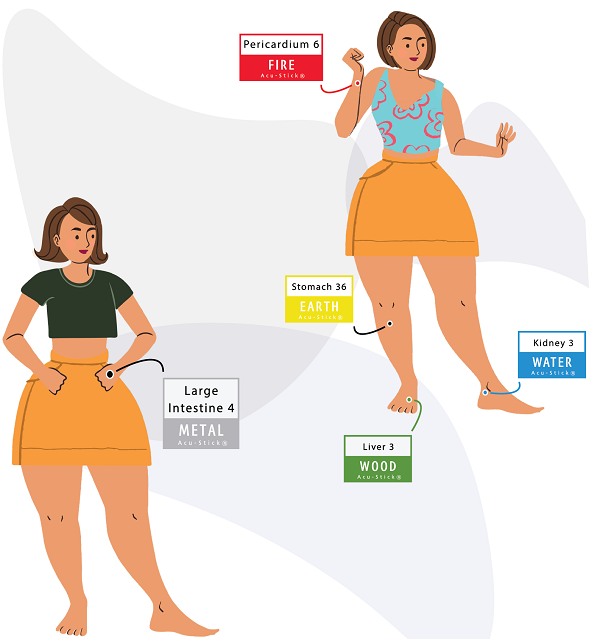
Aroma Acu-therapy™ for Organ-Level Imbalances
Kidney 3
Apply the Water Element Aroma Acu-Stick® to activate Acupressure Point KI 3
Why? Acu-point Kidney 3 is the Source Point of the Kidney energetic organ and is used to nourish Yin of not only the Kidney Organ, but the also the Heart, Liver, Lung Organs according to Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Apply the Earth Element Aroma Acu-Stick® to activate Acupressure Point ST 36
Why? Acu-point Stomach 36 nourishes Qi and Blood of the Stomach and, fortifies the Spleen. It is a major point for boosting the immune system and maintaining wellness.
Apply the Metal Element Aroma Acu-Stick® to activate Acupuncture Point Lung 9
Why? LU 9 is the tonification point for the Lung Energetic Organ System of Chinese medicine.
Apply the Wood Element Aroma Acu-Stick® to activate Acupressure Point LV 3
Why? LV 3 is the energy source point for the Liver energetic organ system that is able to normalize the Liver function as Liver Qi Stagnation is often the root cause of dozens of diseases affecting Organs of the body.
Apply the Fire Element Aroma Acu-Stick® to activate Acupuncture Point Pericardium 6
Why? Acu-point PER 6 regulates Heart Qi and is able to harmonize Stomach and Spleen Qi.
Related Articles:
How to Use Self-care to Balance the Organ Systems, or Zang-Fu of Chinese Medicine
Zang – The Yin organs Kidney, Liver, Heart (Pericardium), Spleen, and Lungs are considered as deeper than the Yang organs, generally more solid, and are involved with the regulation, manufacturing and storage of fundamental substances such as Blood and Essence.
Fu – The Yang organs Stomach, Gall Bladder, Large Intestine, Small Intestines, Bladder, and San Jiao are the hollow organs are viewed as being closer to the surface, or exterior of the body. They are not store substances, and are instead involved with an ongoing process of change through functions of receiving, separating, distributing, and excreting substances.
![]()
Kidney Organ System of Chinese Medicine
- Controls the waterways and regulates fluid balance in the body.
- Stores the Essences (Jing) and produces marrow; this ‘Bone Marrow’ is essential in the formation of bone, the spinal cord, Blood, and the brain.
- Is the base of all Yin and Yang of the body and maintain the Gate of Vitality, or Mingmen Fire.
- Open into the ear and influence hearing, and manifest in the hair reflecting Kidney health through vital, lush, shiny hair.
Common Symptoms of Kidney Imbalances
- Afternoon and night sweats
- Low energy
- Fear, panic attacks, phobias and anxiety
- Premature aging including graying of hair
- Memory loss
- Sexual dysfunctions including impotence
- Infertility
- Urinary disorders
Acupressure Source Point for Kidney
![]()
Liver Organ System
- Opens in to the eyes providing nourishing Liver Blood for vision health.
- Spread Qi of all organs in all directions and allows the free flow of Qi throughout the body necessary for the healthy function of the body.
- Stores Blood and regulates the amount of Blood in circulation, storing and releasing it as bodily demands present themselves.
- Controls tendons and nourishes the tendons and joints with Liver Blood.
Common Symptoms of Liver Imbalances
- Headaches, PMS, anger and frustration
- Acid reflux
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Osteo-arthritis and stiff joints
- Brittle nails
- Lack of vision and direction in planning one’s life
Acupressure Source Point for Liver
- Apply the Wood Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Liver 3
![]()
Heart Organ System
- Governs all emotion
- Sexual warmth
- Controls blood vessels
Common Symptoms of Heart Imbalances
- Emotional instability
- Insomnia
- Palpitations
- Heart disease
- Poor memory
- Mouth and tongue ulcers
Acupressure Source Point for Heart
- Apply the Fire Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Heart 7
![]()
Spleen Organ System
- Controls the raising of Qi
- Contains the Blood
- Transforms and transports foods and fluids
Common Symptoms of Spleen Imbalances
- Poor appetite
- Gas and abdominal distension
- Dampness
- Tiredness or weakness
- Loose stools
- Prolapsed organs
- Uterine bleeding
- Varicose veins
- Easy bruising
- Obsessive worry
- Lack of empathy
Acupressure Source Point for Spleen
![]()
Lung Organ System
- Receives the Qi from the heavens
- Governs over the skin and hair
- Open into the nose
- Controls immune system
Common Symptoms of Lung Imbalances
- Coughing
- Bronchitis, asthma
- COPD
- Sinusitis
- Frequent colds or flu
- Sadness or unresolved grief
- Dogmatism
- Lack of self-worth
- Poor personal boundaries
Acupressure Source Point for Lung
Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Lung 9
![]()
Chinese Medical Concept of Energetic Organ Systems
To a modern westerner, the Chinese concept of organs might seem unusual as the Chinese medical concept of organs lack emphasis on a physical structure. Although many terms used when speaking of organs are similar to western concepts, they do not always refer to the specific organ tissue or structure, but rather to semi-abstract concepts of interrelated functions.
Each organ system has an impact on the other organ systems when it becomes imbalanced; additionally, each organ has an impact on the emotions. Chinese medicine views the individual person as a whole, interactive entity rather than individual parts and pieces. This is how Chinese medicine is able to differentiate disease patterns and devise effective treatment strategies. One disease can have many different patterns depending on a person’s individual body make-up, genetic dispositions, and lifestyle habits. The functions listed are not based on surgical discoveries, but on clinical observation of patients over many thousands of years, making Chinese medicine very practical in actual application.
![]()
Shen, C. Y., Jiang, J. G., Yang, L., Wang, D. W., & Zhu, W. (2017). Anti-ageing active ingredients from herbs and nutraceuticals used in traditional Chinese medicine: pharmacological mechanisms and implications for drug discovery. British journal of pharmacology, 174(11), 1395–1425. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.13631
Chen, Z., Cao, Y., Zhang, Y., & Qiao, Y. (2019). A Novel Discovery: Holistic Efficacy at the Special Organ Level of Pungent Flavored Compounds from Pungent Traditional Chinese Medicine. International journal of molecular sciences, 20(3), 752. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030752
Zhang, W., Tao, Q., Guo, Z., Fu, Y., Chen, X., Shar, P. A., Shahen, M., Zhu, J., Xue, J., Bai, Y., Wu, Z., Wang, Z., Xiao, W., & Wang, Y. (2016). Systems Pharmacology Dissection of the Integrated Treatment for Cardiovascular and Gastrointestinal Disorders by Traditional Chinese Medicine. Scientific reports, 6, 32400. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep32400
Lao, Y. M., Jiang, J. G., & Yan, L. (2009). Application of metabonomic analytical techniques in the modernization and toxicology research of traditional Chinese medicine. British journal of pharmacology, 157(7), 1128–1141. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00257.x
Yang, F., Song, J., Liang, M., Ma, F., Mao, X., Ma, C. W., Zhang, W., & Huang, Z. (2014). Overview of beverages with anti-aging functions in Chinese market. Rejuvenation research, 17(2), 197–200. https://doi.org/10.1089/rej.2013.1514
This information has not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This information is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.





